Monthly Archives: February 2019
In criminal practice and procedure, you might think that the humble adjournment is a relatively simple and straightforward matter, but you would be wrong.
A little like buses, they are never available when you want one. However, when you don’t want a case delayed the court always appears happy to work against you.
In reality, the humble adjournment is now a complex process, and only a mastery of the relevant principles will ensure the best outcome for your case.
The wise advocate is armed with a detailed chronology and will be ready to deploy this information without notice on an unsuspecting opponent. All relevant facts will have been gathered and a detailed submission will ensure the best prospects of success.
On occasion, it will be down to a client to assist. If for example, you cannot attend court due to illness or another unexpected matter arising, your solicitors will ensure that you are aware of the detailed information that needs to be provided.
The case law in relation to adjournments is well known, or at least ought to be. In Crown Prosecution Service v Picton, the High Court detailed the factors that a court ought to focus on:
- A decision whether to adjourn is a decision within the discretion of the trial court. An appellate court will interfere only if very clear grounds for doing so are shown.
- Magistrates should pay great attention to the need for expedition in the prosecution of criminal proceedings; delays are scandalous; they bring the law into disrepute; summary justice should be speedy justice; an application for an adjournment should be rigorously scrutinised.
- Where an adjournment is sought by the prosecution, magistrates must consider both the interest of the defendant in getting the matter dealt with, and the interest of the public that criminal charges should be adjudicated upon, and the guilty convicted as well as the innocent acquitted. With a more serious charge the public interest that there be a trial will carry greater weight.
- Where an adjournment is sought by the accused, the magistrates must consider whether, if it is not granted, he will be able fully to present his defence and, if he will not be able to do so, the degree to which his ability to do so is compromised.
- In considering the competing interests of the parties the magistrates should examine the likely consequences of the proposed adjournment, in particular its likely length, and the need to decide the facts while recollections are fresh.
- The reason that the adjournment is required should be examined and, if it arises through the fault of the party asking for the adjournment, that is a factor against granting the adjournment, carrying weight in accordance with the gravity of the fault. If that party was not at fault, that may favour an adjournment. Likewise, if the party opposing the adjournment has been at fault, that will favour an adjournment.
- The magistrates should take appropriate account of the history of the case, and whether there have been earlier adjournments and at whose request and why.
- Lastly, of course the factors to be considered cannot be comprehensively stated but depend upon the particular circumstances of each case, and they will often overlap. The court’s duty is to do justice between the parties in the circumstances as they have arisen.
What could possibly go wrong with a simple adjournment?
In a recent case of Pari-Jones v Crown Prosecution Service the following facts emerged:
‘On the morning of the trial, the legal adviser to the Magistrates’ Court received two emails from the defence solicitor, which were written in Welsh and were translated and presented to the court. The first email was sent at 9.23am. The solicitor stated that he was acting for the defendant and that she was a lady approaching 80 years old. It was the first listing for trial, and the criminal damage related to a neighbour dispute.
The magistrates were told that the defendant was very concerned regarding the weather, because it was freezing around her house and the road, and she had no electricity. She was living by herself with no close family. The solicitor further wrote that he was stuck in his home, which was in Pwllheli, and that it was freezing hard. He said he was a distance away from the main road, which had been gritted, and although he could leave his house, he was not feeling comfortable in venturing out.’
Almost unbelievably the court refused the defence adjournment and the defendant was convicted in her absence. The magistrates’ admitted to having considered no case law at all!
The full judgement in this case can be found here.
So, what seems to be an unanswerable request for a simple adjournment, in the wrong hands, can go terribly wrong. That is why we train all of our advocates to never take an application for granted and ensure the best advocacy is always deployed on your behalf.
How we can assist
We have a team of highly trained and dedicated solicitors. Unfortunately you’ll see from the facts of the case set out above that the Magistrates don’t always do what to the bystander should be obvious.
If you face court proceedings we can make a real difference to the outcome of your criminal case. Legal aid may well be available to fund your defence at court.
You can find your nearest office here.
Alternatively you can use the contact form below:
Contact
Monthly Archives: February 2019
Raising the issue of modern slavery – can it provide a defence to drug dealing and other criminal offences?
The short answer is: maybe.
Section 45 of the Modern Slavery Act 2015 provides a defence to specific criminal charges where it is shown that they were committed under a compulsion due to slavery or exploitation where a person is 18 or over, or as a direct consequence of slavery or exploitation where a suspect is under 18.
The latter test, for children, is less difficult to establish. It is a defence similar to duress.
This defence could, for example, be used for drugs offences committed as part of a ‘County Lines’ drugs ring.
What else is modern slavery a defence to?
The modern slavery defence can be used for any criminal offence not listed in Schedule 4 of the Modern Slavery Act 2015.
It can’t be used for serious crimes like
- murder
- manslaughter
- kidnapping
- piracy
- serious violence
- firearms offences
- robbery
- burglary
- arson
- criminal damage
- most sexual offences, or
- modern slavery offences themselves.
There are other offences to which the defence does not apply.
It can be used as a defence to any other crime. It is used for victims of ‘County Lines’ drugs offences but also applies to most immigration offences, minor assaults, shop thefts, or conspiracy to do any of these things. Anyone who is trafficked or exploited can potentially benefit from it.
Children may be exploited for a variety of reasons by gangs and used to carry and supply drugs. Children who are particularly vulnerable are often targeted, and they may feel that they can’t tell anyone in case they are arrested and punished.
What needs to be proved?
The defence requires several things, depending on a person’s age. In both cases, they need to be a victim of slavery or exploitation.
Those over 18 rely on s.45(1), where they are not guilty if:
- The crime is committed because they are made to do it
- They are made to do it for some reason connected to the slavery or exploitation
- A reasonable person, with the same characteristics, would not have had a realistic alternative in that situation.
A person under 18 relies on s.45(4), where they are not guilty if:
- The crime is committed as a result of the person being or having been in the past, a victim of slavery or exploitation, and
- A reasonable person, with the same characteristics, would have done the same.
The defence for those under 18 is less difficult to establish, reflecting the increased vulnerability of children.
A person has to raise enough evidence for it to be possible that they are a victim of slavery of exploitation within the meaning of the Act. The prosecution will have to make the Magistrates’ or jury sure that the defence does not apply.
If they cannot, a person then has to show it’s possible that the offence was carried out either under a compulsion relevant to or as a direct consequence of that slavery or exploitation, dependant on the age of the defendant. This, again, will have to be disproved so that the tribunal is sure it does not apply.
If the prosecution cannot disprove either of these things then the defence succeeds.
How can we help you present your defence?
Modern slavery cases are important and sensitive cases to deal with. Our specialist lawyers can advise you on whether you have a defence, and help you put that defence forward, advising on prospects of success and instructing experts to help along the way.
We are experts at dealing with vulnerable clients and children, including many victims of exploitation by ‘County Lines’ drug gangs.
As a result, if you are arrested or know that the police wish to speak to you about a criminal offence and you wish to consider whether you have a defence, make sure you insist on your right to free and independent legal advice.
The advantages of such early legal advice can be found here.
If you have already been interviewed or face court proceedings we can still make a real difference to the outcome of your case. Legal aid may well be available to fund your defence at court.
You can find your nearest office here.

Alternatively you can use the contact form below:
Contact
Monthly Archives: February 2019
Thursday 31 January 2019 was a notable date for the Nottingham legal community as local defence practitioner Finbarr Hennessy retired from practice.
Keeping a low profile
Although having spoken of a wish to retire for some time, his boundless enthusiasm for the job and wish to continue to provide representation for his longstanding client base meant that he continued to delay the inevitable.
In typical fashion, Finbarr sought to keep a low profile, and sought to avoid the (usually) inevitable collection, cards and farewell do. This he managed successfully.
Some thoughts on the changes to the job
Finbarr offered some thoughts on his departure from a job that he still loved:
“It seemed weird walking out of Nottingham Magistrates’ Court this afternoon after spending 23 years of my life in that building.
Video killed the radio star. Technology killed this out-dated solicitor.”
He confessed that he had “struggled since the day that speedy summary justice was introduced at the Magistrates’ Courts”, offering the view that “justice has gone out of the window to be replaced by “progress” and statistics. To get an adjournment is harder than keeping somebody out of prison.”
Additionally he identified that his “lack of technical expertise means that I am now less efficient than I was in 1995.”
Finbarr’s intention had been to ‘go out with a bang’, perhaps collapsing when bail was refused by the Magistrates or when a client had been wrongly sent to prison. Unfortunately for him “I have had good results recently, so my blood pressure has remained stable.”
His final assessment was “We are all replaceable. I only work 14 hours a week and I know that my position will easily be covered.”
No doubt his clients will beg to differ, and will recognise the lengths that he went to on their behalf. Clients and their families had his mobile number and he was effectively on call 24 hours a day, 7 days a week. If families were distressed by the situation that, particularly, youth clients had found themselves in he would visit families at home in his spare time to try and help.
Client feedback on Finbarr Hennessy
Finbarr was described in glowing terms by any number of clients – ‘The solicitor I have is very good at his job’, ‘A1 Service thank you’ and ‘Finbarr Hennessy is an excellent solicitor and needs no improvement’.
It was all the more pleasing to note that following his move to VHS Fletchers when Campion & Co solicitors stopped undertaking criminal work, his clients still found their way to us and continued to receive the high level of service that they would expect.
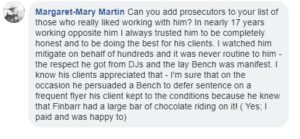
Here a Crown prosecutor offers an opinion on his integrity:
Thoughts from colleagues
Following news of Finbarr’s retirement, partner Jon Hullis said:
“You will always be very fondly remembered by everyone who has had the pleasure to work with you, as well as everyone at court, and especially your clients. You are genuinely the nicest person, and this is proved by the fact that even the police like you.”
Andy Siddall, partner, told Finbarr:
“Some people cannot be replaced.
Your dedication and commitment to your clients should be something all young Solicitors (and indeed some older ones) aspire to. In this dull digital age you will be greatly missed and never forgotten.”
Solicitor advocate William Bennett offered:
“You are and always were a diamond. I wish you weren’t retiring but as you are I wish you well. Rest assured your position will never be “easily covered”. It is hard to cover one of life’s true one-offs. I am grateful to have worked with you.”
A final thought is from partner Nick Walsh:
“Your gift is that you care about people and your colleagues and clients will miss you because of it. Enjoy retirement, it is truly well deserved.”
We will try to continue to provide Finbarr’s clients with the standard of service that they have come to expect, although they will agree that he is irreplaceable.