All posts by Andrew Wesley/h3>
What are the offences?
There are two drug driving offences:
- Driving whilst unfit through drugs
- Driving whilst over the limit for certain drugs
What is driving whilst unfit through drugs?
To be guilty of driving whilst unfit, the prosecution must prove:
- You were driving (or attempting to drive or in charge of) a vehicle on a road or public place; and
- You were unfit to drive; and
- This was due to any drug (medication or illegal)
What is driving over the drug limit?
Since 2015, it has been an offence to drive (or attempt to drive or be in charge of a vehicle) on a road or public place with certain drugs in your blood above fixed limits. Limits have been set for 17 drugs, covering legal and illegal drugs.
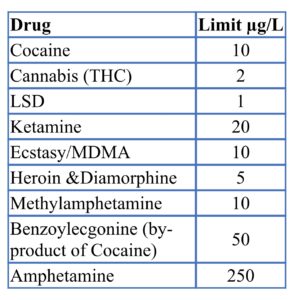
Illegal drugs and the drug driving limit
The limits for illegal drugs are set very low, so that even trace amounts can lead to a prosecution. The limits do not provide any indication that the driver’s behaviour or ability to drive are affected by the drug. As these drugs are illegal, effectively a zero tolerance approach has been adopted.
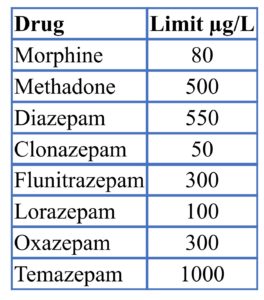
Legal drugs and the drug driving limit
These are prescription or over-the-counter medications. Limits are set at levels where there is an increased risk of road traffic collision and are higher than would be expected in someone who has taken a normal dose as medicine.
What about prescription drugs?
The limits set for legal, medication drugs are lower than would be expected in someone taking a normal dosage of the drug.
For example, people taking Lorazepam as a prescribed medicine would normally have a blood concentration of 10-20 µg per litre of blood. The legal limit is set at 100 µg/L.
Even if your blood sample is over the limit for a drug, providing you are not impaired by it, there is a defence if the drug has been taken for medical purposes. This applies if:
• the drug has been prescribed or supplied for medical purposes; and
• it was taken in accordance with the instructions given; and
• the driver was lawfully in possession of it.
The defence cannot be used where the driver did not follow the instructions about the amount of time that should elapse between taking the drug and driving.
What are the penalties for drug driving offences?
If convicted of a drug driving offence, the court must impose a disqualification from driving for at least 12 months. This can only be reduced or avoided if the court finds that there are “Special Reasons” relating to the offence. The court cannot impose a ban for less than 12 months based on the hardship that would be suffered as a result of it. In addition, the court can impose the following:
• Prison for up to 6 months
• Suspended Prison Sentence
• Community Order
• Unlimited fine
What should I do if I am accused of drug driving?

These are technical offences and involve complicated procedures for the police to follow. Very often, there are mistakes made which mean there is a lack of evidence. Defence experts may be able to challenge the prosecution evidence.
If you would like advice about a drug driving allegation, contact one of the solicitors at your local office or Nottingham road traffic solicitor Graham Heathcote on 0115 9599550 or use the form below.